
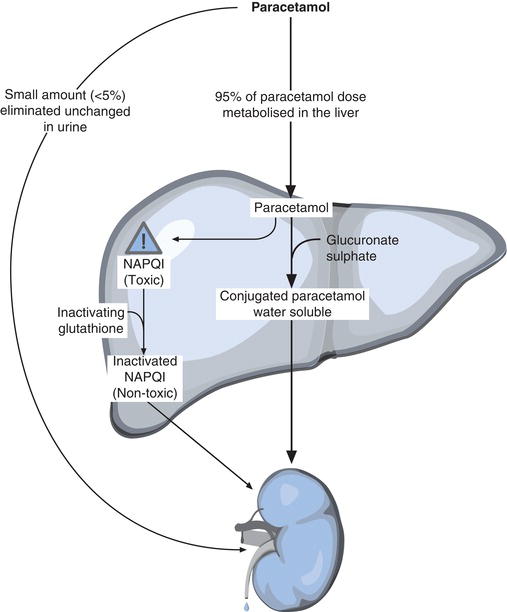
NAC is converted to glutathione, replenishing the reserves.The consequence of this is hepatocellular apoptosis and necrosis.Of particular interest is the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation, which results in a failure of ATP synthesis, lactic acidosis, and the release of ionised calcium from mitochondrial stores.As NAPQI levels increase, it binds covalently to numerous proteins, causing toxicity.


The most satisfying answer is probably found in the 2003 article by James et al, "Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity." It was used as the source for the diagram below. Question 9 from the first paper of 2014 asked "how paracetamol causes liver dysfunction".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
